The rapid evolution of decentralized finance (DeFi) has exposed both the promise and challenges of open blockchain markets. Among the most pressing concerns is Miner Extractable Value (MEV), a phenomenon where validators or miners profit by manipulating transaction ordering, often at the expense of ordinary users. This dynamic has led to front-running, sandwich attacks, and other predatory tactics that undermine user trust and market efficiency. In response, MEV redistribution protocols have emerged as pivotal mechanisms for restoring fairness in DeFi trading.

Understanding MEV and Its Impact on DeFi Trading Fairness
At its core, MEV represents the additional value that can be extracted from reordering, including, or excluding transactions within a block. While some argue that MEV can address inefficiencies in DeFi protocols, it often results in increased slippage, higher transaction costs, and diminished confidence for everyday traders. The ability for select actors to capture outsized profits from transaction sequencing creates an uneven playing field – one that is antithetical to the ethos of decentralized finance.
The latest innovations in blockchain design are tackling this head-on. The FAIR L1 blockchain, for example, integrates encrypted execution at the consensus layer, effectively removing the transparency window that enables MEV extraction (see Blockworks coverage). By embedding privacy into transaction processing, new architectures eliminate opportunities for malicious actors while paving the way for more sophisticated and autonomous DeFi applications.
Key Approaches to Transparent MEV Sharing
The landscape of MEV redistribution protocols is diverse yet unified by a commitment to DeFi trading fairness. Several approaches have gained traction:
Modern MEV Redistribution Protocol Types & Examples
-
Protected Order Flow Mechanisms: PROF (Protected Order Flow) enforces strict transaction sequencing, ensuring transactions are processed in the order received. This prevents front-running and maintains transaction integrity, directly mitigating MEV extraction opportunities.
-

Fair Sequencing Services: Chainlink Fair Sequencing Service (FSS) provides unbiased transaction ordering by removing the ability for miners or validators to reorder transactions for profit. This service significantly reduces MEV by ensuring fair transaction sequencing.
-

MEV Smoothing: Protocols implementing MEV Smoothing pool and evenly distribute MEV rewards among validators or stakers. This approach, used by networks like ZenMEV, reduces income variance and promotes equitable reward sharing across participants.
-
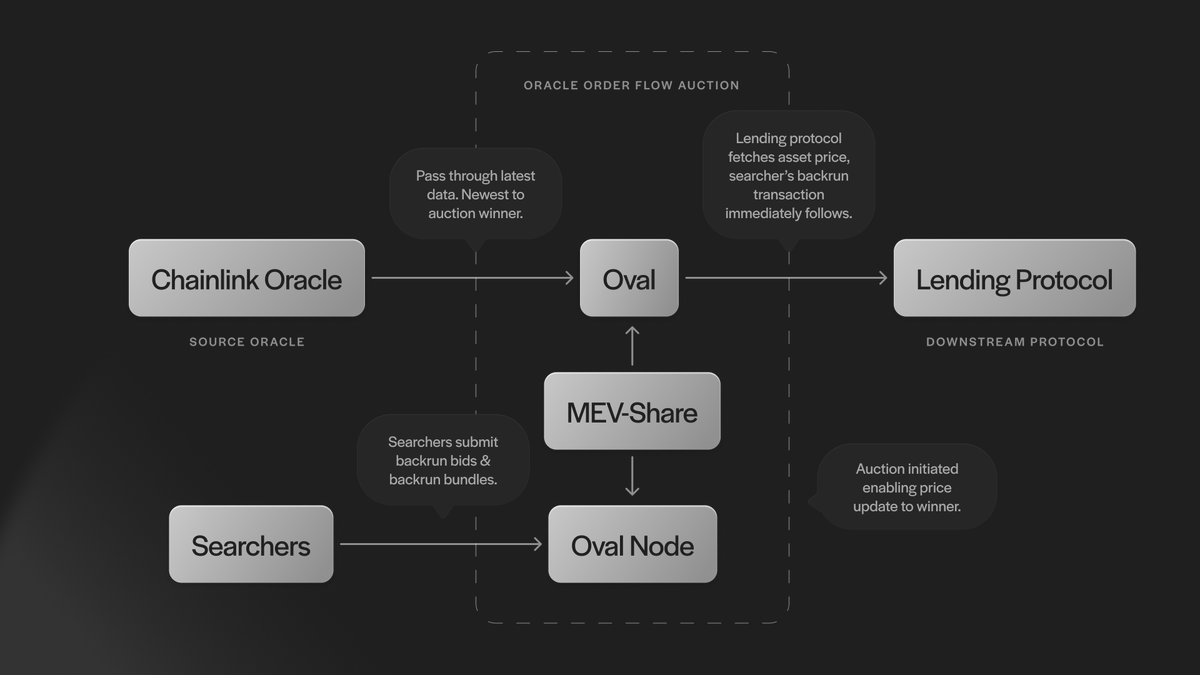
Order Flow Auctions (OFAs): Order Flow Auction mechanisms, as seen in platforms like Flashbots MEV-Share, allow searchers to competitively bid for the right to bundle transactions with user trades. This redistributes a portion of MEV profits back to users, enhancing fairness.
-

Encrypted Mempools and Private Order Flow: FAIR Blockchain leverages encrypted execution at the consensus layer, removing the transparency window that enables MEV. By encrypting transaction data until block finalization, it eliminates front-running and preserves user privacy.
- Protected Order Flow Mechanisms: Systems like PROF enforce strict sequencing based on transaction arrival time, preventing manipulation and ensuring integrity.
- Fair Sequencing Services: Chainlink’s FSS is leading the charge by providing unbiased orderings that minimize opportunities for extractive behavior.
- MEV Smoothing: By pooling rewards and distributing them evenly among validators or stakers, these protocols reduce income variance and foster equitable participation.
- Order Flow Auctions (OFAs): These create competitive environments where searchers bid for block space next to user trades – redistributing value directly back to users.
- Encrypted Mempools and Private Order Flow: Protocols like FAIR Blockchain encrypt transaction data until after block finalization. This innovation eliminates front-running risks by keeping trade intentions private until immutably recorded.
Together, these solutions do more than just mitigate risk; they actively promote transparent MEV sharing and align incentives across network stakeholders. For deeper technical analysis of these mechanisms in practice, see our guide on how MEV redistribution protocols improve fairness in DeFi transactions.
The Benefits of Equitable Value Extraction
The shift toward transparent and equitable value extraction marks a turning point for blockchain-based finance. By capturing what would otherwise be predatory profits and redistributing them among participants – whether through pro-rata staking rewards or direct user rebates – these protocols restore balance to market incentives. As highlighted in recent research from ACM SIGSAC’s DeFi’22 workshop, formal models show that effective MEV redistribution can prevent harmful equilibria where key participants are disincentivized from staking or lending altogether.
This new paradigm not only enhances trust but also reduces overall transaction costs. Users benefit from lower slippage and fewer surprise losses due to adversarial trading tactics. Meanwhile, protocol designers gain tools to foster sustainable growth without compromising security or decentralization.
MEV redistribution protocols are now central to the ongoing professionalization of DeFi infrastructure. By shifting incentives away from opaque, zero-sum extraction and toward shared value creation, these systems help cultivate a more resilient and inclusive trading environment. Notably, approaches like MEV smoothing and order flow auctions do not just redistribute profits, they actively reduce the variance in validator or staker rewards, making network participation less speculative and more attractive for long-term actors.
Emerging privacy-focused blockchains such as FAIR L1 illustrate how technical innovation can fundamentally alter the MEV landscape. By integrating encrypted mempools at the consensus layer, these networks eliminate the transparency window that enables front-running. This breakthrough not only protects users but also unlocks new design space for sophisticated DeFi applications where fairness is embedded at the protocol level.
Challenges and Considerations for Implementation
Despite these advances, implementing effective MEV redistribution protocols is not without its challenges. Protocol designers must balance security, decentralization, and economic incentives while ensuring that solutions remain accessible to both sophisticated traders and retail users. For example, encrypted order flow mechanisms require robust cryptographic primitives and careful coordination among validators to avoid new attack vectors or unintended centralization risks.
Moreover, the success of transparent MEV sharing depends on broad network adoption. If only a subset of validators or searchers participate in fair sequencing or order flow auctions, opportunities for extractive behavior persist elsewhere in the system. This underscores the need for cross-protocol standards and ongoing community education around best practices.
Looking Ahead: The Future of DeFi Trading Fairness
The trajectory of MEV mitigation is clear: as blockchain networks adopt advanced sequencing services and privacy-preserving architectures, predatory extraction becomes less viable while collaborative value capture gains ground. This evolution is already influencing protocol design decisions across major DeFi ecosystems. For investors and developers alike, understanding these changes is essential to navigating risk, and identifying sustainable yield opportunities, in an increasingly complex market landscape.
To stay ahead of these developments and learn more about practical implementation strategies for equitable MEV sharing, explore our definitive guide on how protocol designers can implement MEV redistribution for fairer DeFi ecosystems.
Key Takeaways on Transparent MEV Sharing in DeFi
-

Protected Order Flow Mechanisms like PROF enforce strict transaction sequencing, preventing front-running and ensuring fair trade execution for all users.
-

Fair Sequencing Services such as Chainlink’s Fair Sequencing Service (FSS) provide unbiased transaction ordering, reducing opportunities for MEV extraction by miners or validators.
-

MEV Smoothing pools and redistributes MEV rewards among validators or stakers, promoting equitable value sharing and reducing reward variance across the network.
-

Order Flow Auctions (OFAs) introduce competitive bidding for transaction inclusion, enabling users to receive a portion of MEV profits that would otherwise go to searchers or validators.
-

Encrypted Mempools and Private Order Flow solutions, exemplified by FAIR Blockchain, keep transaction details confidential until block finalization, eliminating front-running and enhancing user privacy.
Ultimately, transparent MEV redistribution protocols are redefining what it means to participate in decentralized finance, moving from a paradigm of unchecked extraction to one of shared prosperity and trust-driven growth.






